10.05.2021
BPMN process mapping - what is it and why should you use it?
Key information:
- There are several methods used to model business processes, but the most popular, which is now an unwritten standard, is BPMN.
- BPMN, or Business Process Model and Notation, is a uniform notation for describing business processes and the relationships linking them.
- One of the main goals of business process mapping is to provide a set of graphical elements with the help of which clear flowcharts are created to visually model the course of business processes.
- The key features of BPMN that determine its success are its unambiguity and universality.
- This notation allows the creation of both simple and very complex flowcharts.
- The purpose of BPMN notation is to improve the management of business processes, make them more transparent and efficient, and enable organizations to better understand, analyze and improve their processes.
- By using BPMN notation, you can arrive at better business process management and increase your organization's competitiveness.
- Collaboration among different stakeholders is key to effective business process modeling and improvement.
- It is worth using the BPMN process mapping method to improve the flow of information in the company and automate the execution of tasks, thus improving the efficiency of the company's operations.
Details below!
Looking at the changes taking place in the modern business world, one can see a gradual decline in the popularity of traditional, functional and rigidly structured enterprise organizations with extensive hierarchies, in which activities are geared toward the performance of individual functions, such as marketing, sales or finance. They are losing their position in favor of forms of organization with a horizontal, horizontal structure in which a process approach dominates. The activities of such companies are not focused on the execution of separate functions, but on managing processes aimed at maximizing customer satisfaction.
Processes in modern organizations are often very elaborate and complex. To make the relationships between them easier to understand, both for members of the organization and outsiders, process mapping is used, that is, individual tasks are extracted and then represented graphically. There are several methods used to model business processes, but the most popular one, which is now an unwritten standard, is BPMN.
What is BPMN?
BPMN, or Business Process Model and Notation, is a uniform notation for describing business processes and the relationships linking them. One of its main goals is to provide a set of graphical elements with which to create clear flowcharts for visually modeling the flow of business processes.
If you need advice on implementing innovations schedule a free consultation and together we will determine how we can help your business.
What makes this notation so valued and so widely used?
The key features of BPMN that determine its success are its unambiguity and universality. This notation allows the creation of both simple and very complex flowcharts. Thanks to its standard graphical form, it can be understood by users from different organizations, working in different positions - from managers to business analysts to programmers. BPMN is also compatible with dozens of process modeling and automation programs, such as MS Visio, iGrafx, ARIS and TIBCO Business Studio, among others.
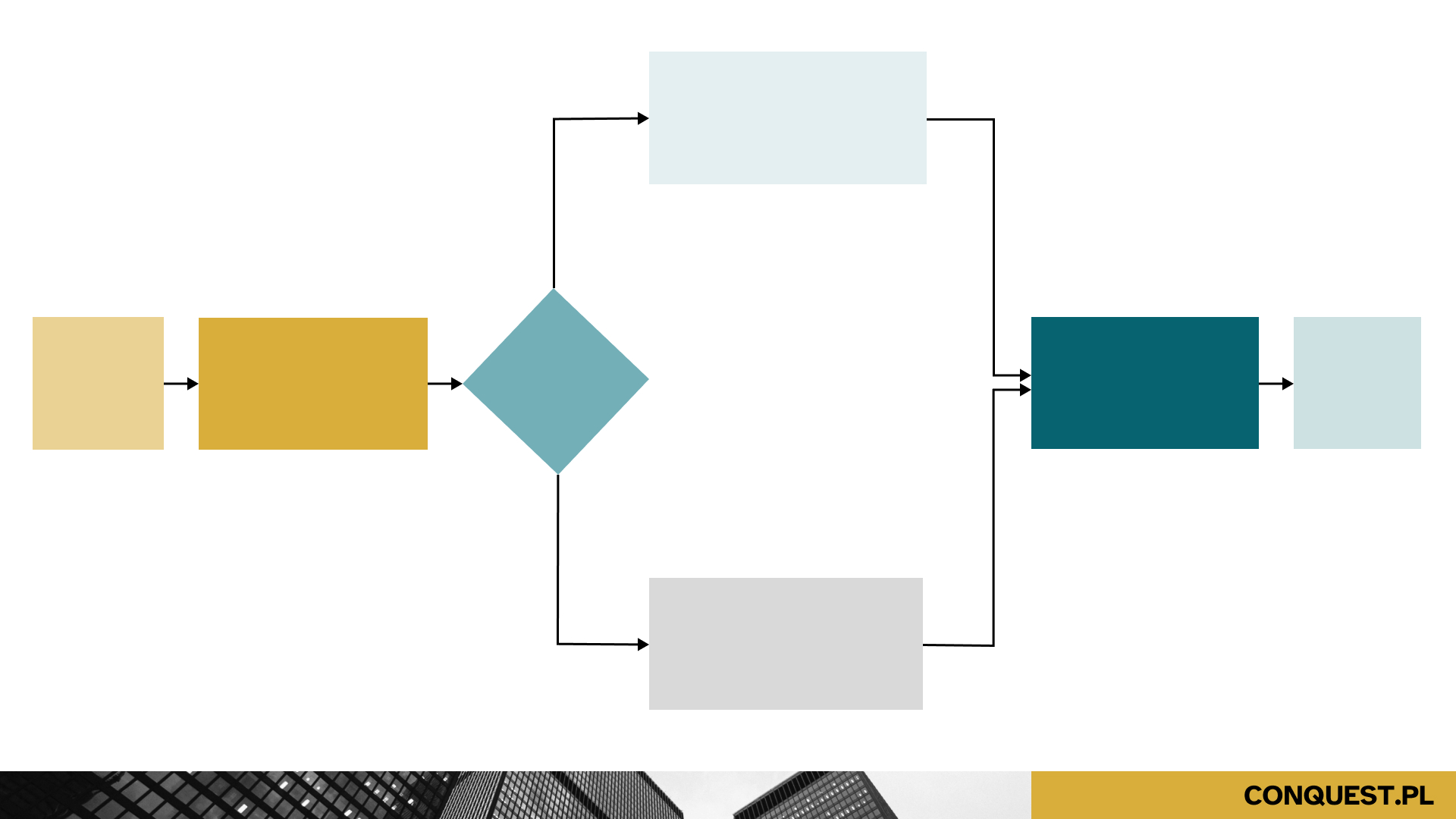
How to create a BPMN diagram?
What are the goals of BPMN notation?
BPMN notation aims to provide a uniform and understandable way to represent business processes in organizations. The main tasks of BPMN notation include:
- Clear representation of business processes: BPMN allows business processes to be represented graphically and intuitively. This makes it easy for people from different disciplines and levels of the organization to understand how a process works.
- Standardization: BPMN is an industry standard, which means it is widely accepted and used in business environments around the world. This allows organizations to avoid confusion and errors resulting from different ways of representing processes.
- Communication: BPMN notation enables effective communication between different stakeholders in an organization, such as managers, process analysts, developers and end users. This allows everyone to stay informed about what processes are and how they work.
- Automation: BPMN can be used to automate business processes. Processes written in BPMN notation can be easily converted into executable models that can be run and controlled using business process management (BPM) software.
- Optimization: With process representation in the form of BPMN diagrams, organizations can more easily analyze and optimize their business processes. They can identify where there are delays, errors or unnecessary steps and take action to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Decision-making support: BPMN can be used to model alternative business process scenarios. This helps organizations make more informed decisions about process changes.
- Easy training: BPMN notation is relatively easy to learn and use, making it easy to train employees and introduce it to the organization.
In summary, the purpose of the BPMN notation is to streamlining managing business processes, increasing their transparency and efficiency, and enabling organizations to better understand, analyze and improve their processes.
Benefits of BPMN
There are many benefits to using BPMN modeling. Key among them is transparency, or the ability to clearly represent business processes through graphical diagrams, which facilitates understanding and communication. BPMN is also a global standard, which facilitates collaboration between organizations. It allows automation of processes, which increases efficiency and eliminates errors. Creating process diagrams helps identify and eliminate unnecessary steps, improving efficiency, and is a great support for decision-making. By using BPMN notation, you can arrive at better management of business processes and increase the competitiveness of your organization.

Elements of BPMN notation
The graphical elements used in BPMN notation can be divided into four categories. The first of these is objects related to the process flow -. actions, which are the tasks to be performed by a person or system; events, which mark the beginning, middle and end of a process; and gates, also known as decision objects, which describe the flow path of a sequence in a process. The second is made up of connecting elements, which are used to bind the objects of the process and show its progress. The third category is grouping objects other elements. They are called variously - tanks or pools. Each pool is further divided into tracks that show the responsibilities and location of events that occur in it. The fourth group is expansion elements, such as annotations of various kinds.
Processes highlighted in BPMN notation
The BPMN notation distinguishes several types of processes. The first of these is private trials, also referred to by the term "workflow". These are internal activities, specific to a particular organization. These processes should be presented within a single pool. The only elements that can cross boundaries are messages, for the exchange of information between different private processes. A good example of such a process is the receipt of correspondence in a company - its elements are consecutive activities, such as the receipt of a message in a box, the preparation of a response and the sending of a return message.
Another type is public trials. They show the interactions that occur between a private process and participants outside of it. The purpose of this model is to make limited information available to a process. An example would be the flow of messages between two separate pools - one that deals with receiving messages in a certain company's Customer Service Department and another that introduces a customer to it.
The next model, collaboration, presents two or more pools containing processes and the interactions that occur between them. Using the earlier example, the event of sending a message in the private process "Customer" is combined with the event of receiving a message in the process "Company Customer Service."
The last of the models, choreography, describes the interactions that occur between two or more participants in the process. But importantly, it does not describe the activities that the individual participants perform.

Who does process modeling?
Business process modeling is a complex process that involves various roles and departments within an organization. Analysts are key; they analyze, design and optimize activities using BPMN notation. Process managers oversee process efficiency, and engineers implement model-based changes. Directors and department managers make strategic decisions about processes. IT specialists are responsible for automating processes, and end users provide feedback. This collaboration between different stakeholders is crucial for effective business process modeling and improvement.
How to plan a process using BPMN?
Wanting to graphically represent a process flow using BPMN notation, the first step is to identify the processes. For this purpose, you can use the top-down method, in which the overall activity of the organization is determined and individual elements are specified on the basis of it, or the more difficult but more precise bottom-up method, in which the course of processes is formulated, based on the analysis of activities performed in the organization.
The next step is to divide processes into main and auxiliary processes. Then, out of all the processes, you have to distinguish those that are crucial for achieving specific business goals. Finally, a detailed process map is created that shows all the activities that make up the process.
A well-prepared BPMN process map allows you to present even the most complicated and complex business processes in a clear and easy-to-understand way.
It is worth using this method to streamline the flow of information in the company and automate the execution of tasks, thus improving the efficiency of the company's operations.




